Information for the General Public

Deep Venous Thrombosis
Deep
venous
thrombosis
often
shortened
DVT
occurs
when
blood
clots
in
a
deep
vein
of
the
leg.
It
affects
nearly
2
million
people
in
USA
every
year
and
many
die
from
resulting
pulmonary
embolism
when the clot breaks off from the leg and moves to the lung.
Normally
blood
flows
freely
through
veins.
When
the
flow
is
interrupted
either
by
injury
or
by
compression
of
the
vein,
the
blood beyond the point of compression can clot.
People at Risk of DVT:
•
Soon after major surgery involving the hip, knee or leg
•
After fractures of large bones in the leg
•
Patients confined to bed after any major surgery
•
Anyone who is bedridden for prolonged periods
•
Women on contraceptive Pills
•
Pregnancy and childbirth
•
Varicose veins
•
Airline passengers confined to their seats on long haul flights
Generally
the
older
you
are
the
greater
the
chances
of
developing
DVT.
It
is
said
that
the
chances
double
with
each
decade
of life after 40.
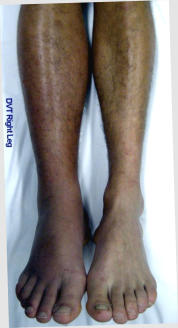
Symptoms:
•
Swollen leg compared to opposite leg
•
Leg may be warm and red
•
Pain in the calf muscle particularly when pressure is applied
•
Chest pain or difficulty to breathe if the clot moves to the lung
Tests for DVT:
Clinical examination may suggest a possible DVT. This should be confirmed by one or two tests.
•
Ultrasound: US will usually confirm a blocked vein from a clot.
•
D-dimer blood test: If the level of D-Dimer is raised, it is probable that you have DVT.
•
Venography is sometimes done if the ultra sound is not very clear.
•
Sometimes MRI or CT scan may be requested.
•
If pulmonary embolism is suspected a Ventilation/Perfusion scan is done.
Preventing DVT:
Steps should always be taken to prevent a DVT rather than worry about it when it happens.
In
a
hospital
setting
most
of
the
patients
who
are
subjected
to
major
lower
limb
surgery
will
be
prescribed
blood
thinning
medication and maintained on it until they start walking normally.
In
many
countries
all
patients
admitted
to
hospital
are
also
given
anti
embolism
stockings
to
wear.
These
are
elastic
stockings
that provide uniform compression for the leg preventing pooling of blood in the veins when they are in bed.