

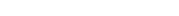
HEPATITIS
(This article should help the general public to understand how the disease spreads)
Hepatitis is a term used to describe inflammation (swelling) of the liver.
It can occur as the result of a viral infection or because the liver is exposed to harmful substances such as alcohol.
Some types of hepatitis will pass without causing permanent damage to the liver. Other types can persist for many years and
cause scarring of the liver (cirrhosis). In the most serious cases, it may lead to loss of liver function (liver failure) or liver cancer,
which can both be fatal. These types of long-lasting hepatitis are known as chronic hepatitis.
Initial symptoms: (similar to the flu)
•
muscle and joint pain
•
a high temperature (fever) of 38ºC (100.4ºF) or above
•
feeling sick
•
being sick
•
headache
•
occasionally, yellowing of the eyes and skin (jaundice)
Symptoms of chronic hepatitis:
•
feeling unusually tired all the time
•
depression
•
jaundice
•
a general sense of feeling unwell
In many cases hepatitis causes no noticeable symptoms, so when hepatitis is caused by a virus, many people are unaware they
are infected. Similarly, many people with hepatitis caused by alcohol are unaware that their drinking is harming their liver.
Types of hepatitis: A, B, C, D and E
Hepatitis A: caused by the hepatitis A virus, is the most common type of viral hepatitis. It is more common in countries where
sanitation and sewage disposal are poor. Infection with Hepatitis A usually occurs by eating food contaminated by faeces of
someone with hepatitis A. Contamination can happen when preparing food with dirty hands. Infection can also occur through
water that is contaminated with sewage carrying the infection. This often occurs in countries like India and China.
Infection is usually short-term (acute) and symptoms will pass within three months. There is no specific treatment for hepatitis A
other than to relieve symptoms. A vaccination can protect you against hepatitis A.
Vaccination is recommended if you are travelling to countries where the virus is common, such as the Indian subcontinent,
China, Africa, Central and South America, the Far East and Eastern Europe.
Hepatitis B: caused by the hepatitis B virus. This can be found in blood and
body fluids, such as semen and vaginal fluids, so it can be spread during
unprotected sex, by sharing needles to inject drugs, and from pregnant women
to their babies. Hepatitis B is uncommon in England and cases are largely
confined to certain groups, such as drug users. It is much more common in
other parts of the world, particularly East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa.
Most people infected with hepatitis B are able to fight off the virus and fully
recover from the infection within a couple of months. However, a small minority
of people develop a long-term infection. This is known as chronic hepatitis B. In
some people, chronic hepatitis B can cause cirrhosis and liver cancer. Chronic
hepatitis B is treatable with antiviral medication.
A vaccination is available for preventing hepatitis B, which is recommended for
people in high-risk groups, such as injecting drug users or healthcare workers.
Hepatitis C: It is the most common type of viral hepatitis in England. It is caused by the hepatitis C virus. This can be found in
the blood and, to a much lesser extent, the saliva and semen or vaginal fluid of an infected person.
It is particularly concentrated in the blood, so it is usually transmitted through blood-to-blood contact.
In some countries it's most commonly spread through sharing needles by drug addicts.
Hepatitis C often causes no noticeable symptoms, or symptoms that are mistaken for the flu, so many people are unaware they
are infected. Around one in four people will fight off the infection and will be free of the virus. In the remaining three out of four
people, the virus will stay in their body for many years. This is known as chronic hepatitis C. In some people, chronic hepatitis C
can cause cirrhosis and liver failure.
Chronic hepatitis C can be treated by taking antiviral medications, although there can be unpleasant side effects. There is
Information for the General Public