Health
of
any
human
being
is
dependent
on
the
state
of
6
major
organs
in
the
body.
They
are
the
brain,
the
heart,
the
lungs,
the
liver,
the
pancreas
and
the
kidneys.
Although
there
are
other
organs
that
also
help
maintain
normal
health
majority
of
the
problems
are
caused
by
pathology
affecting
one
of
the
6 organs.
Important functions performed by the kidney:
•
Excretion of toxic waste formed in the body
•
Important in regulating blood pressure
•
Maintenance of salt and water balance in the body
•
Role
in
the
synthesis
of
vitamin
D
and
production
of
red
blood
cells
(RBC)
Kidneys
produce
urine
through
which
most
of
the
waste
products
formed
in
the
body
are
excreted.
If
the
kidneys
malfunction,
toxic
waste
products
start
to
accumulate
causing
ill
health.
The
kidneys
are
also
responsible
for
maintaining
the
right
amount
of
salt
and
water
in
the
body
(electrolyte
balance).
Any
imbalance
in
the
electrolyte
levels
can
again
cause
serious
ill
health
ranging from lethargy to unconsciousness and cardiac arrest.
How does the Kidney function:
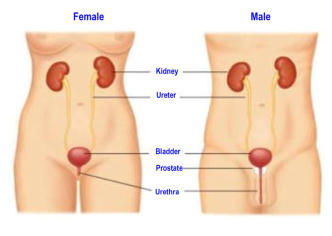
Normally
there
are
2
kidneys
through
which
a
large
volume
of
circulating
blood
flows
through.
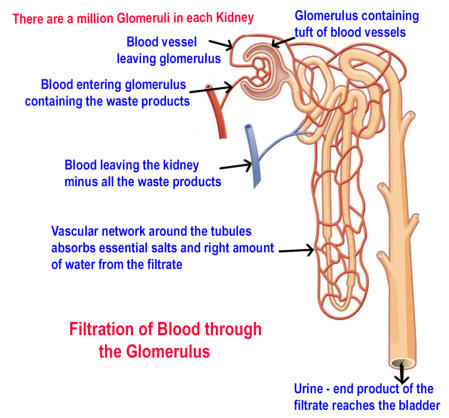
The
blood
containing
salts,
waste
products
and
all
the
other
components
flow
through
tiny
blood
vessels
bundled
together
in
structures
called
glomerulus.
These
are
the
specialised
filtering
units
in
the
kidney.
There
are
approximately
1
million
glomeruli
in
each
kidney.
The
fluid
that
is
filtered
from
blood
passes
through
a
series
of
tubules.
As
the
filtrate
flows
through
the
tubules,
all
essential
salts
together
with
the
right
amount
of
water
is
reabsorbed
back
in
to
the
circulation.
The
rest
of
the
water
together
with
the
toxic
waste products pass through the ureter and stored in the bladder to be excreted later as urine.
Urine
is
an
ultrafiltrate
of
blood
plasma.
It
is
slightly
acidic
and
normally
will
not
contain
blood,
protein
or
sugar.
If
any
of
these are present it indicates an underlying disease.
If
the
glomeruli
or
tubules
are
affected
by
disease,
chemicals
or
poison,
the
kidney
function
will
be
impaired
resulting
in
accumulation
of
toxins,
waste
products
and
excess
water.
The
electrolyte
balance
will
also
be
affected.
The
result
is
kidney
failure.
The
grade
of
failure
will
depend on the extent of damage.
Kidneys Can Be Damaged by:
•
Environmental Pollutants
•
Severe Dehydration
•
Trauma to the Kidney
•
Myoglobin
released
when
muscles
are
crushed
during an accident
•
Hypertension
•
Diabetes Mellitus
•
Cancer
•
Anti inflammatory Drugs like Ibuprofen
•
Antibiotics like Gentamycin
•
Iodine containing medications used in scans.
Symptoms of Kidney Failure:
•
Lethargy
•
Tiredness
•
Breathlessness
•
Loss of appetite
•
Generalised swelling (oedema)
•
Puffiness of face
•
Palpitation
•
Feeling fait
Checking Your Renal Function
Renal
or
kidney
function
tests
(RFTs)
are
done
to
assess
how
well
the
kidneys
are
working.
The
tests
are
done
when
there
is
suspicion
of
impaired
kidney
function
or
it
is
done
as
part
of
a
routine
health
check.
If
done
as
part
of
a
routine
health
check
a
Kidney Function